Bloody Discharge: Causes and How to Treat It
Monique Rainford, MD, is board-certified in obstetrics-gynecology, and currently serves as an Assistant Clinical Professor at Yale Medicine. She is the former chief of obstetrics-gynecology at Yale Health.
Learn about our Medical Review BoardTable of ContentsView AllTable of ContentsSeeing bloody discharge when you’re not expecting it can be alarming. But bloody discharge can be normal and isn’t always a sign of an emergency. Age, lifestyle, and medical history all come into play when determining the cause of bleeding.
This article will explain common causes of bloody discharge, when to see a healthcare provider, and how to treat or prevent it in the future.
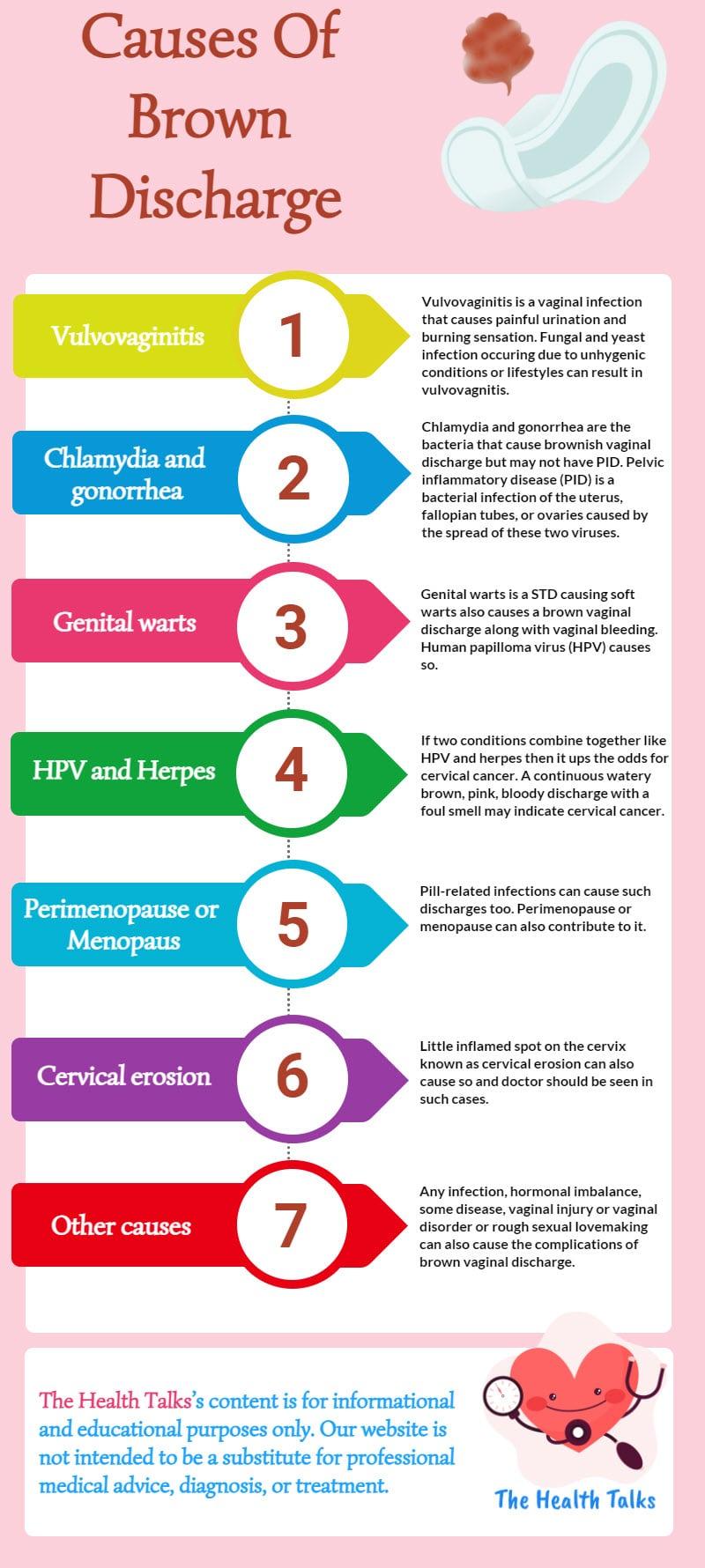
Causes of Bloody Discharge
Bloody discharge does not always indicate that something is wrong. In fact, there are many cases where it points to normal bodily responses.
Menstrual Cycle
Menstruation, the shedding of the uterine lining, is the most common form of bloody discharge. It can indicate the beginning of your menstrual cycle or period. A regular period occurs, on average, every 28 days or about 14 days after regular ovulation.
The color of your period may change during your cycle, starting with pink, brown, or black blood and transition into burgundy or red blood.
During Early Puberty
Age is often a factor in irregular menstruation. Menarche, or the onset of menstruation, is a normal process that usually occurs around the age of 12 in girls.
After getting your first period, it's common to not get another period for a few months, causing bloody discharge to appear on an irregular schedule. This is because it can take a while for the hormone cycle that is responsible for ovulation and regular menstruation to mature.
Perimenopause and HT
Perimenopause is the phase leading up to menopause—or your last period. In general, most women begin noticing perimenopausal symptoms in their 40s, with the average age being 47 years old.Menstrual cycle changes are normal during perimenopause. Your periods may be shorter, longer, heavier, or lighter than usual. You may even miss some periods.
Hormone therapy, or HT, refers to a combination of the female hormones estrogen and/or progesterone medication. Some women may be prescribed these to lessen perimenopause and menopause symptoms. One known side effect of HT is irregular bleeding.
Pregnancy-Related
While bleeding during pregnancy may be a problem, it's actually quite common during the first trimester, or first three months of a normal pregnancy.

About 15% to 25% of pregnant women have bleeding in the first trimester. The bleeding is typically light and occurs after fertilization (when the fertilized egg implants in the lining of your uterus). This type of bleeding is also sometimes called implantation bleeding and isn't cause for concern.
While implantation bleeding is common, always check in with your healthcare provider about bleeding during pregnancy because it can be an indication of something more serious.
Concerning Causes of Bloody Discharge
In some cases, bloody discharge or bleeding between periods can point to more severe conditions. In all cases, it's important to track your symptoms holistically and see your healthcare provider, as bloody discharge is often one of many symptoms that help lead to a diagnosis.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a chronic inflammatory condition in which tissue normally found in the uterine lining forms in other organs of a woman’s reproductive or endocrine system.Symptoms vary in severity and can cause irregular menstrual bleeding or spotting between periods. Endometriosis is challenging to diagnose, so it’s important to monitor other symptoms like severe cramps, unexplained pelvic pain, painful sex, fatigue, and bladder problems.
Cancer
Many common cancers experienced by women rarely cause symptoms at early stages. If early symptoms do occur, it’s often bleeding or spotting outside of menstruation.
Burst Ovarian Cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms within or on top of an ovary. They are common and usually resolve on their own, but in some cases can burst and be associated with abnormal bleeding or bloody discharge.
A burst ovarian cyst will usually cause sharp and sudden pain located on one side of the pelvis. This often happens after sex or strenuous activity.
Infectious Causes
Pregnancy Problems
While bleeding during early pregnancy is common, you should always check in with your healthcare provider because in some cases it can be cause for concern.
Thyroid Disease
The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the front of your neck. In addition to controlling metabolism, heart rate, and other functions, the thyroid hormone plays an essential role in reproductive health.
Women are 10 times more likely to develop thyroid disease than men, which can lead to complications in menstruation. Too much or too little thyroid hormone can make your periods very light, heavy, or irregular. Thyroid disease also can cause your periods to stop for several months or longer, a condition called amenorrhea.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a chronic condition that affects about 1 in 10 women of childbearing age and can impair fertility. The symptoms of PCOS vary making this chronic disease so confusing.
One common symptom of PCOS is irregular, absent, or heavy menstruation. That's because people with PCOS typically have higher levels of male hormones called androgens, which throw off the ratio of female sex hormones (like the ones that control your menstrual cycle).
This can lead to absent periods for several months or irregular ones that may come two or more times in one month.
Obstructive Causes
Bleeding doesn’t always point to a medical condition. Sometimes common obstructions can cause bloody discharge.
Anatomical Causes
Bloody discharge can also point to benign growths or masses in the genital region.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
Any unexplained vaginal bleeding between periods is a reason to see your healthcare provider. It is especially important if you haven't yet gone through puberty, if you are past menopause, or if you are pregnant.
If menstruating, your healthcare provider might ask you questions about when it occurs, how long it lasts, and how heavy the bleeding is. Consider keeping track of your cycle using an app, a calendar, or a diary.
In addition, your healthcare provider may ask questions about any other symptoms you’re experiencing. So monitoring any pain, dizziness, or other discharge will help direct them to a cause.
To help diagnose your bloody discharge, they may perform a pelvic exam, blood tests, colposcopy, ultrasound, hysteroscopy, or other diagnostic tests.
Summary
Bloody discharge can be normal and isn’t always a sign of an emergency. There are many cases where it is a normal body response. When bloody discharge occurs during menopause, later in pregnancy, or is accompanied by other symptoms, it may point to a more severe condition. Age, lifestyle, and medical history all come into play when determining the cause of bleeding outside of menstruation, so it's important to track your symptoms and see your healthcare provider.
A Word From Verywell
Seeing blood in your underwear when you're not expecting it can be alarming. Our bodies are in constant communication with us, using symptoms to clue us into natural processes or unusual conditions. When it comes to bloody discharge, it's not always bad news. Keeping track of your period is a simple way to help understand the cycles of your body, what's normal for you, and what should be flagged.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?Thanks for your feedback!Sign up for our Health Tip of the Day newsletter, and receive daily tips that will help you live your healthiest life.
You're in!Thank you, {{form.email}}, for signing up.
There was an error. Please try again.
What are your concerns?21 SourcesVerywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.